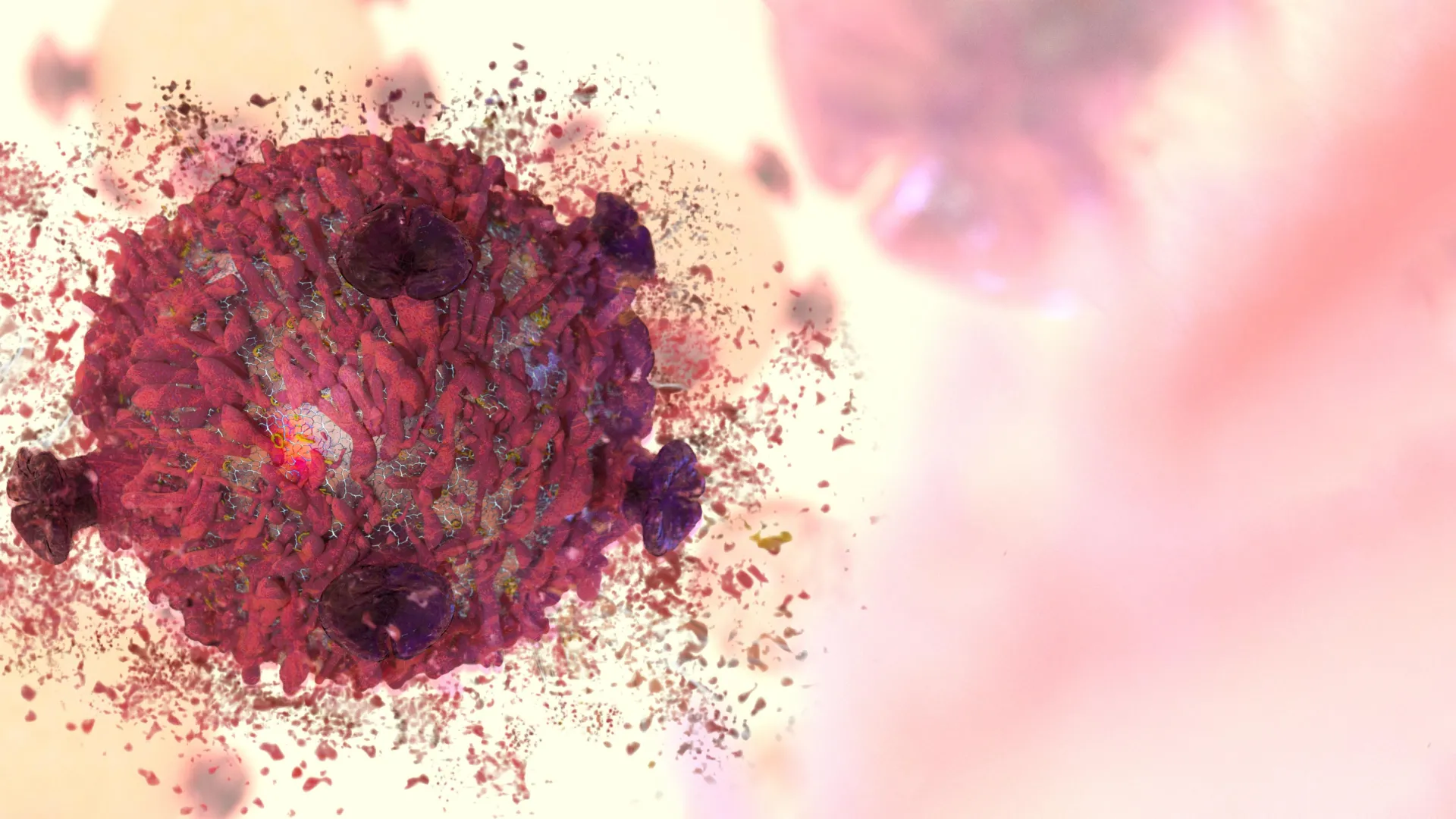
Blocking a single protein forces cancer cells to self-destruct
Researchers uncovered a powerful weakness in lung cancer by shutting down a protein that helps tumors survive stress. When this protein, FSP1, was blocked, lung tumors in mice shrank dramatically, with many cancer cells essentially triggering their own self-destruct mode. The work points to a fresh strategy for targeting stubborn lung cancers. Source link