Scientists find 15 gut bacteria that may drive heart disease
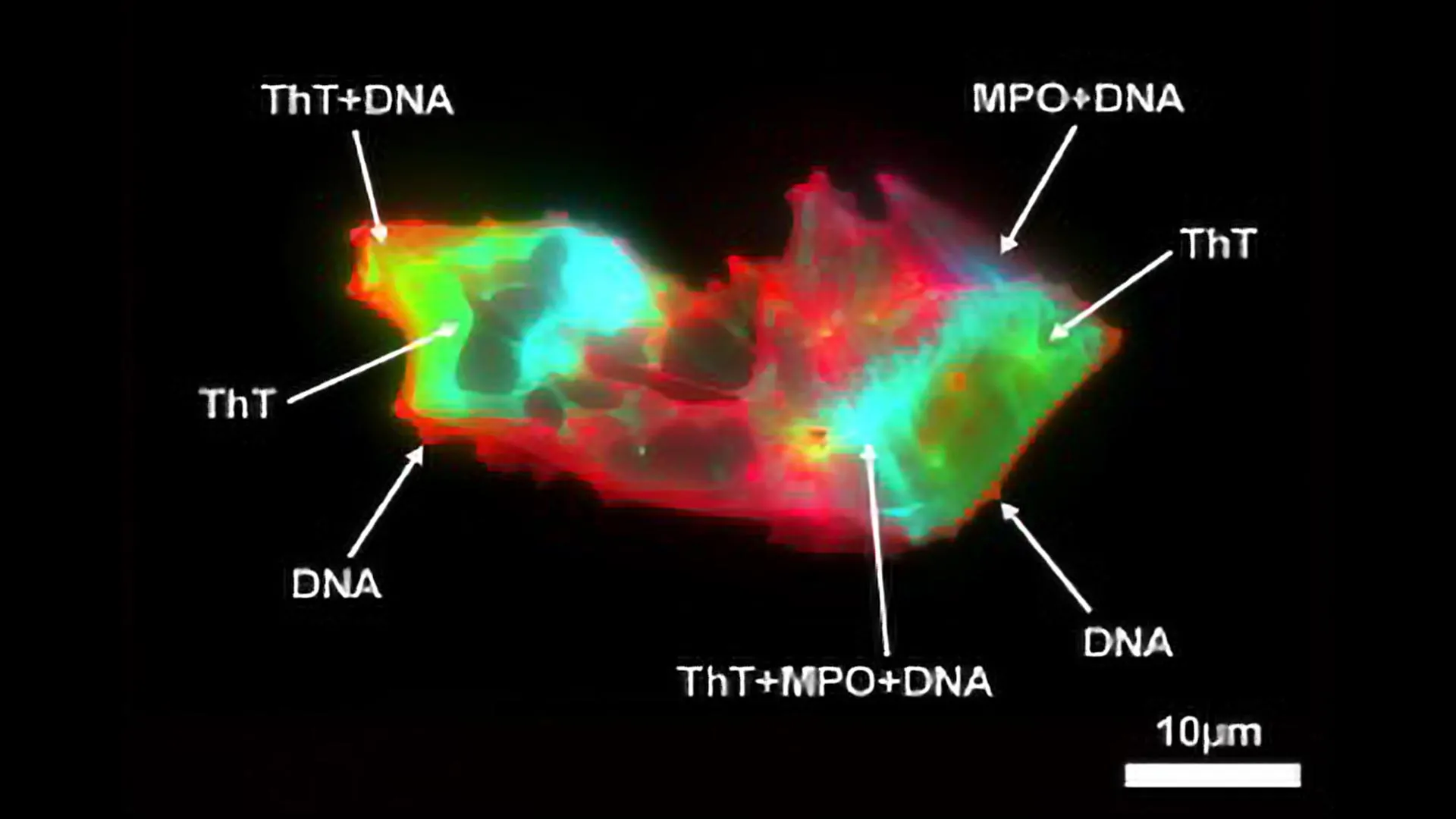
Scientists in Seoul have uncovered 15 gut bacterial species linked to coronary artery disease, showing that microbes can influence heart health far beyond digestion. Their findings reveal how shifts in gut microbial function — including inflammation, loss of protective species, and overactive metabolic pathways — may drive disease progression. Intriguingly, even “good” bacteria like Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Akkermansia muciniphila can become harmful under certain conditions. Source link